Heat pumps offer an energy-efficient, low carbon solution to heating and hot water demand.
Due to poor design and installation heat pumps often get a bad reputation and are labelled a new unproven technology. In fact you can trace the development of heat pumps back to the mid-1750’s,100 years before the first working steam boiler! With thorough design and installation over the period of a year they can exceed 350% efficiency.

How Does a Heat Pump Work?
Heat pumps use environmental energy to generate heating and hot water for your home. They work by extracting thermal energy (heat) from the air, ground or a local water source, which is then converted by a heat pump to generate heating and hot water for your home.
which is then converted by a heat pump to generate heating and hot water for your home.
Based on figures generated in September 2022 heat pumps emit an average of 43% less CO2 than a gas boiler. This will improve as the UK moves towards its goal to decarbonise the electricity system by 2035.

Evaporator
The environmental heat is carried from the outside to the heat ex-changer, causing the refrigerant to evaporate into a gas

Compressor
The refrigerant is then compressed, increasing the temperate to one that is high enough for use.

Condenser
The heat is then transferred to the heating system through the refrigerant gas, condensing it back to a lig-uid. The generated heat will move from the heating system through the homes chosen emitter system (such as underfloor heating or compatible radiators)

Expansion Valve
The now-liquid refrigerant will then decrease the pressure (and therefore the temperature) by passing through the expansion valve. This then restarts the cycle
Types of Heat Pump
There are multiple types of heat pump that can be used and the best one will likely depend on your home location and surrounding environment. Heat pumps can use air, ground, or water sources to generate hot water and heating for your home.
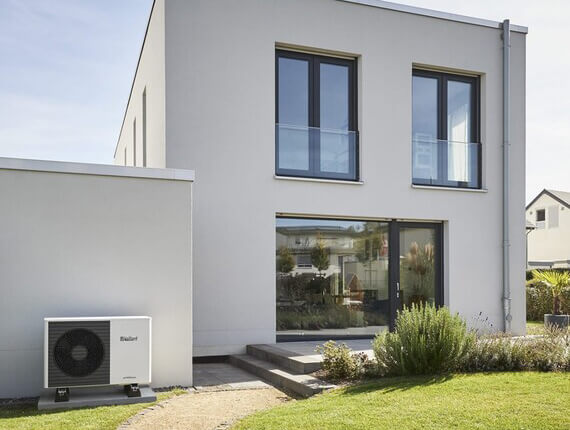


Air to water Heat Pumps
An air source heat pump, sometimes referred to as an air-to-water source heat pump, transfers heat from the outside air to water, which heats your rooms via radiators or underfloor heating. It can also heat water stored in a hot water cylinder for your hot taps, showers and baths.
Some electricity energy is required to allow this, though it is only around 25% of the total energy used during the process. Air source heat pumps will operate in low temperatures too.
Air to Water heat pumps are most commonly used in the UK. Using the October 2022 price cap rates can be cost neutral in 5 years when compared to a gas boiler.

Air to Air Heat Pumps
Air-to-air heat pumps transfer heat from the outside air to air inside your home, increasing or decreasing the temperature of the air in each room. This conditioned air enters your home through a single or series of indoor units.
Air-to-air heat pumps are sometimes referred to as air conditioning. While many people think of air conditioning as a way of cooling buildings, it can also be used for heating but not hot water.
Some electricity energy is required to allow this, though it is only around 25% of the total energy used during the process. Air source heat pumps will operate in low temperatures too.

Ground Source Heat Pumps
Ground source heat pumps use a system embedded into the ground to extract heat. For this reason, your home does need the necessary land to allow installation of either a ground array or borehole system. Installed systems are not noticeable once completed. Some electricity energy is required to allow this, though it is only around 25% of the total energy used during the process.

Water Source Heat Pumps
Water source heat pumps use a system embedded in a water source to extract heat. Water source heat pumps often provide the most reliable source of hot water and heating in homes, thanks to the consistent water temperatures outside. Additionally, installed water source systems are the most low-profile and are best used in instances where visuals must be preserved at all costs. Some electricity energy is required to allow this, though it is only around 25% of the total energy used during the process.
Hybrid Systems
A hybrid heating and hot water system is a combination of two or more technologies generating heat together as a low carbon alternative for home heating.
These typically consist of a gas or oil boiler and an air to water heat pump.
The heat pump is expected to generate heat for 70-80% of the time and, during high demand, the boiler acts as a top-up, giving all year-round comfort.
Although we would always recommend insulating your building to the highest standards many UK homes are generally not that efficient with relatively poor fabric insulation and glazing – this can make a standalone heat pump potentially unsuitable.
Hybrid heat pumps however can be more flexible to accommodate a wider variety of system requirements, making them a viable option for less thermally efficient homes, or applications where a higher flow temperature is required.



